In the era where digital security is paramount, understanding the landscape of cyber threats is essential. We strive to stay up-to-date with the latest changes and trends by following the leading authorities in cybercrime analysis, which provides comprehensive data to shed light on the current state of online security threats. Some of the crucial resources in this endeavor are valuable insights into the ever-evolving tactics of cybercriminals, analysis of phishing attacks and other identity theft techniques, and the evolution and proliferation of identity theft methods by drawing from the research of industry experts.
Phishing Defined
Phishing is a sophisticated cybercrime that combines social engineering tactics and technical manipulation to illicitly acquire consumers’ personal identity information and financial account details. It involves tricking individuals into thinking they interact with a reputable entity through deceptive emails and fake websites. These emails and sites are cleverly crafted to coax users into revealing sensitive financial information like usernames and passwords. On the technical side, phishing employs malware to harvest credentials from users’ computers directly, often by rerouting them to bogus websites or intercepting login details. This extended approach to phishing highlights its dual nature, leveraging both psychological manipulation and technological exploitation.
Phishing Activity Trends Summary
- In the second quarter of 2023, the APWG observed 1,286,208 phishing attacks. This was the third-highest quarterly total that the APWG has ever recorded. However, phishing trended downward.
- The average wire transfer amount requested in BEC attacks in Q2 2023 was $293,359. This was up 57 percent from Q1’s average of $187,053.
- The financial sector remained the most-attacked sector, with 23.5 percent of all phishing attacks. Attacks against online payment services were another 5.8 percent of all attacks.
- Voice-mail phishing or vishing volume continues to rise.
Several Key Metrics to Assess the Global Prevalence and Nature of Phishing Activities:
- Unique Phishing Sites: This metric is crucial for understanding the global scope of reported phishing. The distinct base URLs identified in the phishing emails collected in the repository form the basis for this analysis. Notably, a single phishing operation can use multiple URLs pointing to the same fraudulent site, making the count of unique sites a more relevant measure than simply counting URLs.
- Unique Phishing Email Subjects: This involves counting the variety of email subjects used in phishing lures. Different phishing campaigns might employ identical subject lines while directing victims to various phishing sites. This measure provides an overview of phishing attacks’ diversity and potential scale.
- Number of Brands Targeted: reports also examine the variety of brands impacted by phishing, analyzing the reports submitted. This involves standardizing the brand names to accurately count and assess the breadth of targeted brands.
Collectively, these metrics provide a comprehensive view of the phishing landscape, offering insights into the tactics and scale of these cyber threats.
| April | May | June | |
| Number of unique phishing Web sites (attacks) detected | 597,789 | 381,572 | 306,847 |
| Unique phishing email campaigns | 41,083 | 30,717 | 22,610 |
| Number of brands targeted by phishing campaigns | 544 | 521 | 498 |
In the second quarter of 2023, APWG observed 1,286,208 phishing attacks. This was down from the 1,624,144 attacks seen in 1Q 2023, which was the record-high quarter in their historical observations. The 2Q 2023 total was the third-highest quarterly tally the APWG has ever observed. It was much higher than the 888,585 in 4Q 2022, equal to the 1,270,883 phishing attacks in 3Q 2022. However, phishing fell notably by the end of the second quarter. The 306,847 attacks seen in June 2023 were the smallest monthly total since November 2021.
The number of phishing sites seen over the last year was:
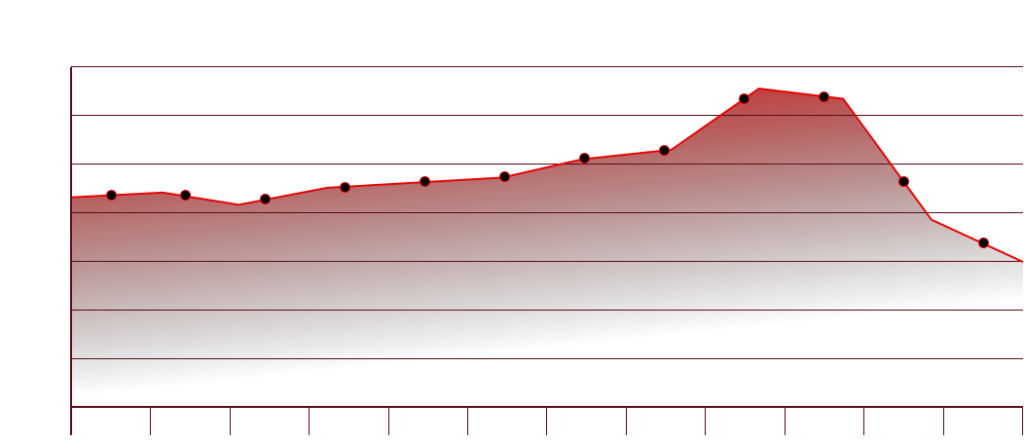
In the second quarter of 2023, there was a notable decrease in the diversity of phishing campaigns, as evidenced by the reduction in unique email subject lines. The average number of distinct email campaigns per month, which had exceeded 40,000 in the first quarter of 2023, saw a significant decline. Similarly, the total number of email reports received by the Anti-Phishing Working Group also fell, with the count in June being just over half of what was recorded in April. This suggests a downward trend in phishing activities during this period.
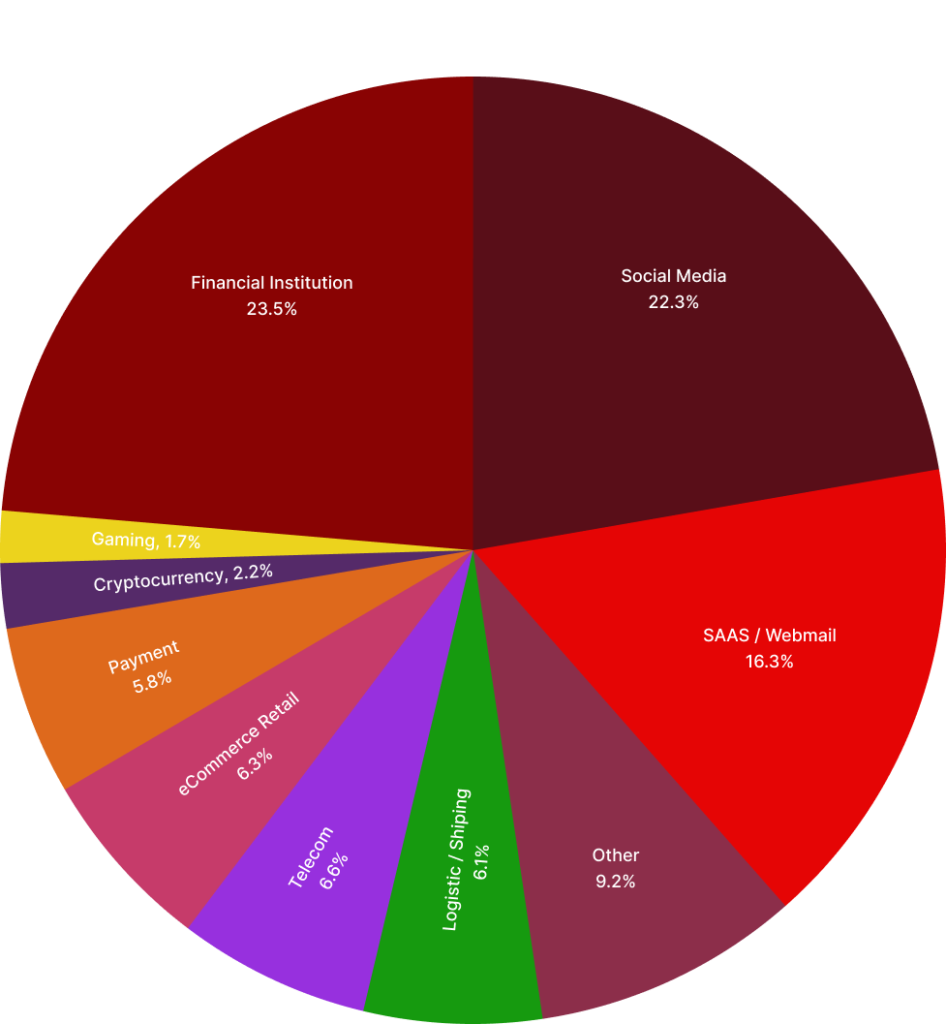
Most-Targeted Industry Sectors – 2nd Quarter 2023
During the second quarter of 2023, OpSec Security, reported that phishing attacks on the financial sector, including banks, continued to be predominant, representing 23.5% of all phishing attacks, a figure unchanged from the first quarter of 2023. Furthermore, attacks on online payment services constituted an additional 5.8% of total attacks. Notably, phishing incidents targeting social media companies have seen a significant rise, accounting for 22.3% of global attacks in the second quarter, up from 18.2% in the first quarter of 2023. This marks a steady increase from 15.5% in the second quarter of 2022 and a considerable jump from just 8.5% in the fourth quarter of 2021. There was also a noted decrease in fraud volume from the first to the second quarter of 2023.
Matthew Harris, Senior Product Manager, Fraud at OpSec Security, noted:
The SAAS/Webmail category fell to third in our ranking, primarily driven by a reduction in the number of phish targeting Microsoft Outlook.
Harris added:
Continuing trends we observed in 2022, we’re again tracking a strong increase in mobile phone-based fraud, or voice phishing. The volume of ‘vishing’ continues to rise. Quarter-over-quarter, we are seeing a steady 10 percent increase in the number of companies being targeted by vishing.
Business e-Mail Compromise (BEC), 2nd Quarter 2023
The FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3) reports staggering losses of $50.8 billion from October 2013 to December 2022 due to BEC (business email compromise) attacks. In these attacks, fraudsters impersonate a trusted entity via email to deceive employees into transferring funds or sensitive information. The analysis of Q2 2023 revealed a significant rise in the average amount requested in wire transfer BEC attacks, reaching $293,359, a 57% increase from the previous quarter.
Despite a 29% drop in the volume of such attacks, the focus seems to have shifted to targeting higher-value transactions. Advance fee fraud scams were the most common method for cashing out, followed by requests for gift cards, with Amazon and Apple Store cards being particularly favored. Payroll diversion also remained a significant attack vector.
In the second quarter, the rise of hybrid vishing (voice phishing) as a new form of attack was noticed, constituting 5% of the response-based attacks they observed. This type of attack combines traditional voice call phishing with other methods, such as email, to trick victims more effectively. This trend indicates an evolution in phishing techniques, where attackers are blending various strategies to increase their chances of success.
John Wilson, Senior Fellow, Threat Research, said:
The hybrid vishing attacks we track typically begin as an email stating that the recipient has been charged for a product or service. The message instructs the recipient to call a phone number if they wish to cancel the order and obtain a refund. PayPal was the most common brand used as a lure in these attacks, making up 38 percent of the total. This was followed by Geek Squad, McAfee, and Norton/LifeLock each with 19 percent of cases we observed.
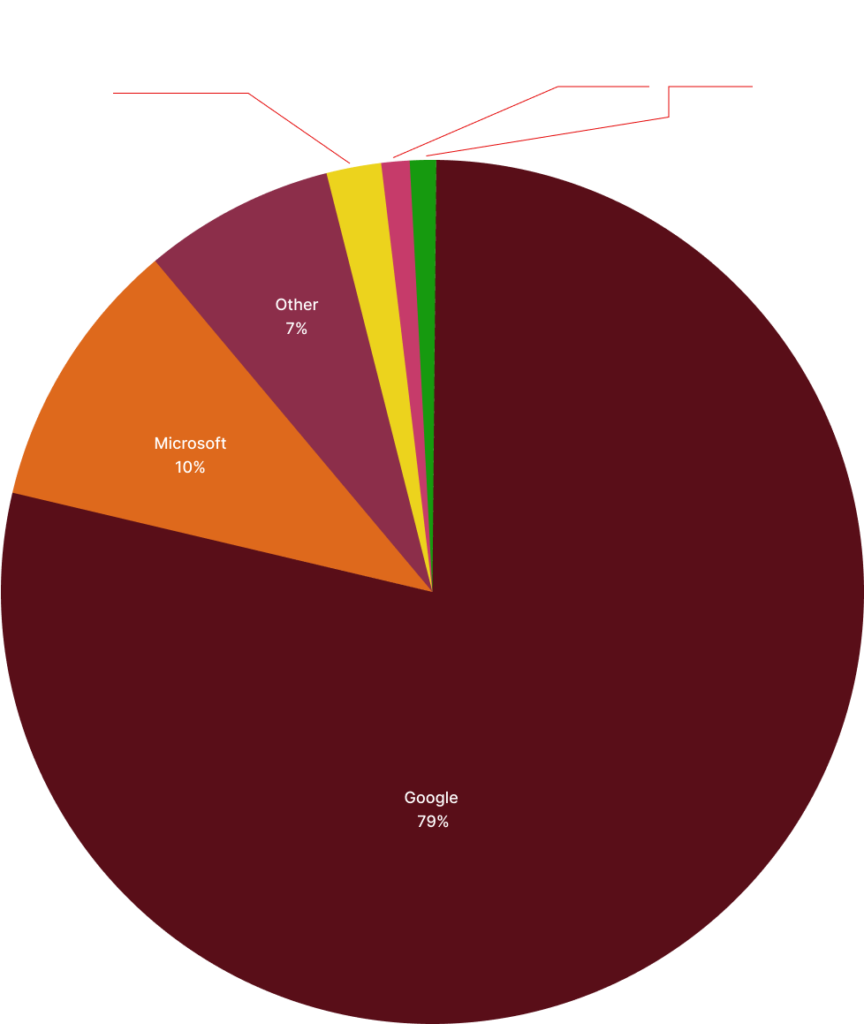
In the second quarter of 2023, researchers discovered a significant shift in the methods used for Business Email Compromise (BEC) attacks. They found that 87% of these attacks were executed using free webmail addresses, marking an increase from 73% in the same quarter of the previous year. The other 13% of BEC attacks involved the use of domains that were either maliciously registered or comprised of compromised email accounts. Notably, Google’s Gmail was the most favored email service among BEC scammers, being used in 79% of the free webmail-based BEC scams during this period, which is a 7% increase from the previous year. Additionally, Microsoft’s webmail services were used for 10% of these attacks, while Verizon Media’s email services, which include Yahoo and AOL, were involved in only 2% of BEC attacks using free webmail accounts in Q2 2023.
Conclusion
The rising prevalence of phishing on social media highlights an urgent need for heightened cybersecurity measures. As these platforms become increasingly integral to our daily communications, they also become more attractive targets for cybercriminals. Individuals and organizations must prioritize digital literacy, recognizing the sophisticated nature of these threats and adopting robust security practices. The implementation of advanced security features by social media companies, along with ongoing user education, is essential for safeguarding personal and financial information in the digital realm. The fight against phishing is a continuous one, requiring vigilance and collaboration across all sectors to effectively combat these evolving cyber threats.
