In the ever-evolving world of cybersecurity, staying ahead of emerging threats is crucial for businesses of all sizes. Today, we’re witnessing a dramatic shift in the nature of cyber threats, influenced by technological advancements and changing digital landscapes.
According to Gartner, in 2023, ransomware continued its upward trend, increasing by almost 14% – an increase as large as in the last five years combined (a total of 25% this year).
It is important to remember that ransomware itself is actually just a model for monetizing an organization’s access. Blocking the four key paths mentioned above helps block the most common routes that ransomware uses to infiltrate your network.

Ransomware: The Persistent Threat
Ransomware attacks have evolved from mere nuisances to sophisticated, targeted operations. These attacks no longer just encrypt data but also threaten to leak sensitive information, adding an extra layer of coercion. Key Mitigation Strategies include:
- Regular Backups: Ensure regular, secure backups of critical data.
- Employee Training: Educate staff on recognizing phishing attempts, a common ransomware entry point.
- Patch Management: Keep all systems updated to patch vulnerabilities.
Phishing: The Chameleon of Cyber Threats
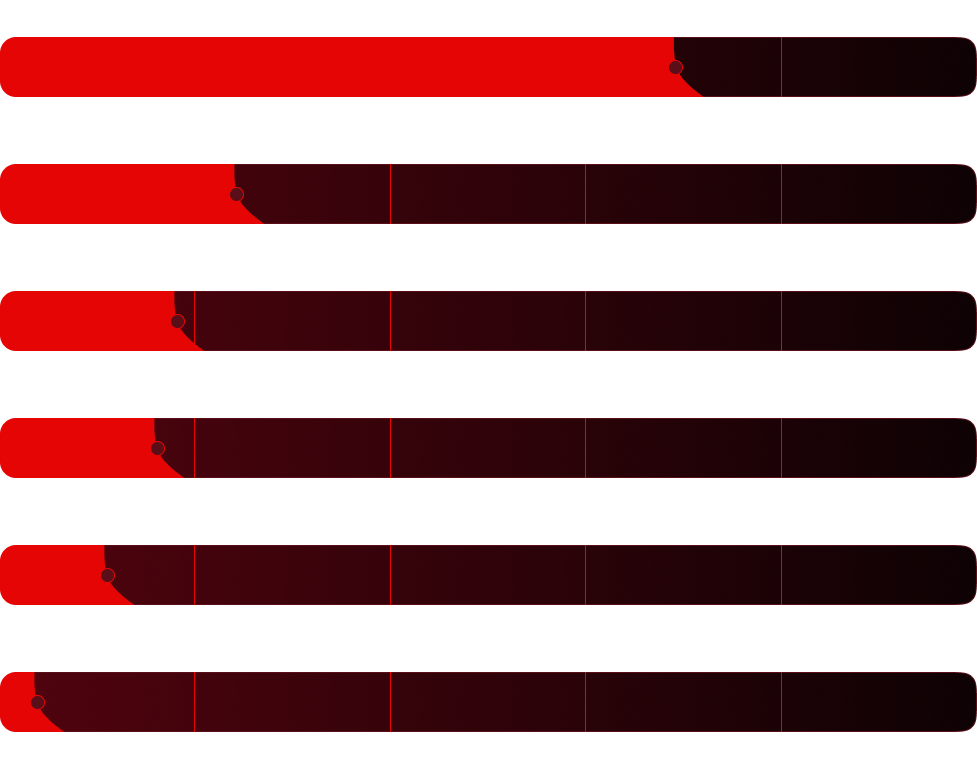
Phishing remains a primary vector for cyber-attacks, adapting rapidly to evade detection. As this graph shows, more than 60% of all hacks are phishing , followed by identity theft (potentially collected through phishing) and ransomware (potentially related to phishing). Given the key importance of this industry to our daily well—being, we certainly hope that these credentials are not the only thing that ensures the security of our utilities and mining enterprises, especially since this is one of the most frequently hacked types of data. Given the high prevalence of phishing and credential attacks, it is not surprising that email servers are the most frequently hacked asset in this industry, followed by web applications and desktop computers. Despite the fact that the infrastructure on which these complex systems operate is not a traditional IT infrastructure, a company can still be exposed to the same threats as any other organization.
Spear-phishing, targeting specific individuals with tailored messages, and whaling, focusing on high-profile targets, are particularly concerning. Protection measures involve:
- Advanced Email Filtering: Utilize AI-driven email filtering solutions.
- User Education: Continuously train employees to recognize and report phishing attempts.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Implement MFA to add an extra security layer.
AI-Driven Cyber Attacks: The Emerging Front
AI and machine learning are not just tools for defenders but also for attackers. AI-driven attacks can automate target selection, craft more convincing phishing messages, and even find and exploit vulnerabilities faster than ever before. Defensive Strategies include:
- AI in Defense: Employ AI-based security tools for real-time threat detection and response.
- Threat Intelligence: Stay informed about AI-driven threat tactics and indicators.
- Ethical AI Frameworks: Develop and adhere to ethical AI usage guidelines in cybersecurity measures.
IoT and Smart Device Vulnerabilities
The proliferation of IoT devices has opened new frontiers for cyber threats. Many of these devices lack robust security, making them easy targets. Securing IoT requires:
- Device Management: Maintain an inventory of all IoT devices and their security postures.
- Network Segmentation: Segregate IoT devices from critical network segments.
- Regular Updates: Ensure firmware and software of IoT devices are regularly updated.
Cloud Security: The New Normal
As businesses increasingly rely on cloud services, cloud security becomes paramount. Misconfigurations, inadequate access controls, and compromised credentials are common issues. Cloud Security Best Practices involve:
- Comprehensive Access Policies: Implement strict access controls and regularly review permissions.
- Cloud Security Solutions: Use tools specifically designed for cloud security monitoring and management.
- Regular Audits: Conduct periodic security audits of cloud environments.
Conclusion: Proactive Defense as the Way Forward
The key to combating these evolving cyber threats lies in a proactive, multi-layered defense strategy. This includes staying informed about the latest trends, investing in advanced security solutions, and fostering a security-conscious culture within the organization. Remember, in the realm of cybersecurity, vigilance and continuous adaptation are not just choices but necessities.
Businesses must embrace these challenges as opportunities to strengthen their security posture, ensuring resilience in the face of a dynamic threat landscape. With the right strategies and tools, organizations can not only defend against these threats but also thrive in this digital era.
